-
×
 The Last eCom Course with Justing Phillips
1 × 27,00 $
The Last eCom Course with Justing Phillips
1 × 27,00 $
The Measurement Matrix with Chris Mercer
39,00 $
You may check content proof of “The Measurement Matrix with Chris Mercer” below:
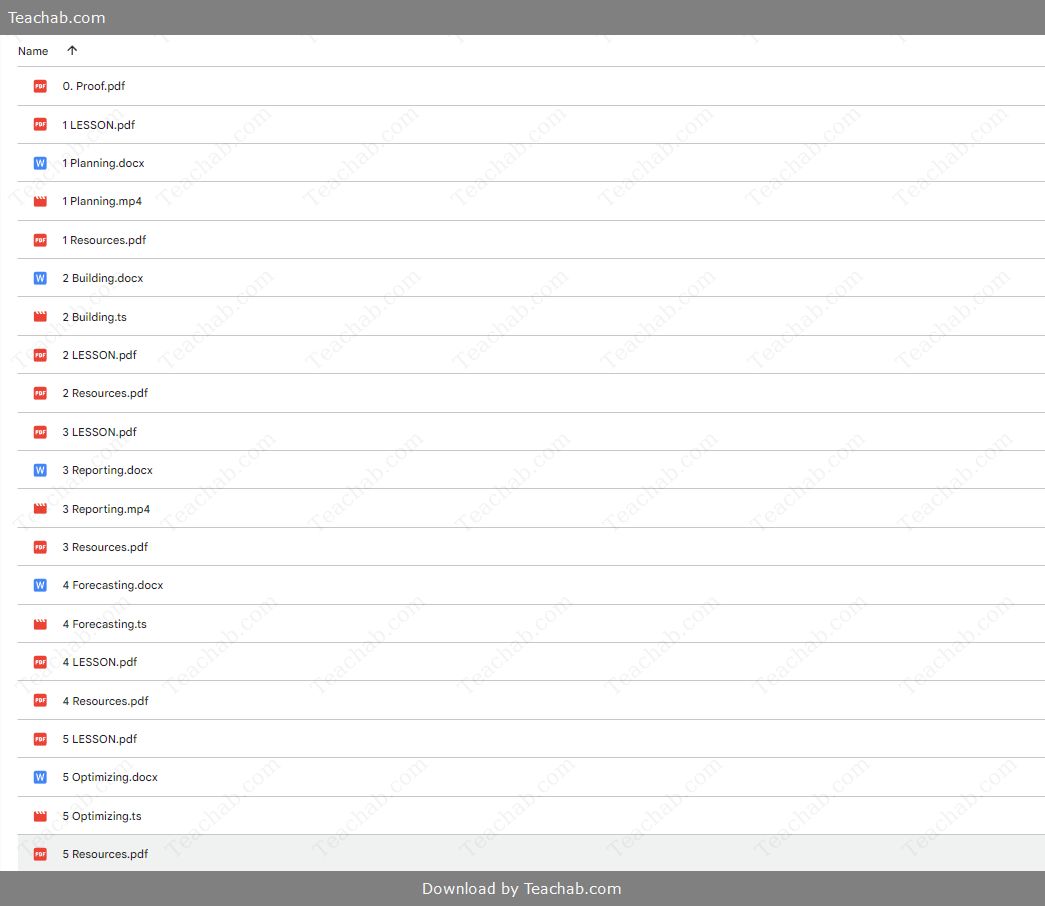
The Measurement Matrix by Chris Mercer
In the fast-paced world of marketing, data has become both a valuable asset and a crucial cornerstone for decision-making. Chris Mercer, the co-founder of MeasurementMarketing.io, has pioneered what is known as the Measurement Matrix a robust framework designed to optimize marketing measurement practices. This framework intricately combines thorough planning, data collection, reporting, evaluation, and optimization to help organizations get the most out of their marketing efforts.
Mercer emphasizes that understanding what to measure is as essential as measurement itself. The Measurement Matrix operates on the principle that accurate and actionable metrics are fundamental for driving marketing success. By providing a structured approach, marketers can systematically analyze their data, leading to improved decision-making and increased return on investment (ROI). The landscape of marketing is ever-changing, and Mercer’s framework provides a roadmap to navigate these complexities effectively. The Measurement Matrix is not merely about data; it’s about translating that data into meaningful actions that align with business goals.
Below, we delve deeper into the various components of the Measurement Matrix, explore its significance in today’s data-driven environment, the best practices for effective reporting, and dissect real-world applications of the framework.
Understanding the Measurement Matrix Framework
At its core, the Measurement Matrix offers a structured approach to marketing metrics, emphasizing the significance of integrated measurement strategies. Much like a compass that provides direction on a journey, the framework helps marketers stay on course by aligning measurement activities with their overarching business objectives. Just as a traveler would not embark on a journey without knowing their destination, marketers too must clarify what they want to achieve before diving into data collection.
The framework revolves around several critical stages planning, building, reporting, and optimizing. Each of these elements is interconnected, forming a holistic approach crucial for proper analysis and actionable insights. For instance, if the planning stage lacks clarity, the subsequent stages risk becoming misaligned with the intended goals. The analogy of a well-constructed architecture applies perfectly here: without a solid foundation (planning), the overall structure (data strategy and measurement) is likely to crumble under pressure.
Moreover, Mercer’s approach is vital in an era where data overload can paralyze decision-making. By practicably sifting through relevant data, organizations can transform simple metrics into insights that not only demonstrate past performance but also predict future trends. The emotional connection provided by well-researched data resonates with stakeholders, breaking down silos that often separate departments and fostering a unified approach to achieving measurable results.
Key Components of the Measurement Matrix
The pinwheel of the Measurement Matrix features several integral components, each spinning towards more refined data-driven decisions. These components include:
- Planning: At the inception, careful planning identifies the questions that need answering, the information required, and the corresponding actions to take based on the insights gained. This Q.I.A. framework ensures that every step taken aligns with business objectives.
- Building: This is where the blueprint from the planning phase turns into action. Marketers construct the measurement infrastructure, which involves setting up tools, defining key performance indicators (KPIs), and ensuring that data integrity is maintained throughout.
- Reporting & Analysis: Once data is collected, this component focuses on interpreting those metrics into meaningful insights. Reports crafted efficiently ensure stakeholders understand how well marketing initiatives meet established goals.
- Optimizing: The measurement cycle is cumulative; insights gained from reporting lead to refinements in strategies, creating a feedback loop that continually informs and enhances marketing efforts.
These components highlight the intricate relationship between planning, execution, and analysis in marketing measurement. Without each element working in harmony, a brand’s ability to successfully navigate market dynamics becomes significantly hindered.
Importance of Planning in Measurement
Planning is the bedrock upon which the Measurement Matrix stands. It is the preliminary phase that not only sets the direction for all subsequent activities but also ensures that measurement efforts are strategically aligned with business goals. Understanding desired outcomes and defining what success looks like is vital for effective measurement. It parallels setting a destination for a journey: without a clear end goal, the route taken can become haphazard and directionless.
Marketers that engage in rigorous planning often find that their activities yield far more insightful outcomes. During this phase, the identification of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is critical. KPIs serve as milestones that guide marketers in assessing progress towards goals, allowing for course corrections as necessary. By delineating specific KPIs, marketers can pinpoint areas needing attention and efficiently allocate resources to those areas.
Studies show that organizations that practice structured planning witness heightened levels of data accuracy, which ultimately helps in decision-making. A systematic approach, such as leveraging the Q.I.A. method, fosters accountability and permits future-oriented thinking. When strategies are clearly defined, teams can pivot quickly in response to data insights, making use of real-time information to drive ongoing marketing tactics.
Think of planning within the framework as assembling a jigsaw puzzle: a clear vision of the final image guides the assembly process. Without the picture, individual pieces may not fit together, resulting in frustration and confusion. In a similar vein, well-articulated planning ensures that each aspect of measurement aligns with overall organizational objectives, leaving no room for ambiguity or misalignment. This commitment to planning translates into a strengthened foundation for measurement success, paving the way for effective data usage in marketing strategies.
Building Effective Measurement Strategies
Once marketers establish a solid planning foundation, the next critical phase is building effective measurement strategies. This stage involves the implementation of systems for gathering, storing, and analyzing data in a structured manner. It’s akin to constructing a house: the planning phase determines the layout, while this phase focuses on erecting the building itself.
Creating a comprehensive measurement strategy necessitates identifying the tools required for data collection and ensuring that metrics align with the KPIs set during the planning process. Failure to build a robust strategy can lead to ineffective data collection, making it challenging to derive actionable insights that inform marketing tactics.
Here are some essential factors to consider when building measurement strategies:
- Reliable Data Sources: Establishing reliable channels for data collection ensures that marketers capture accurate and relevant information. This might involve integrating analytics platforms like Google Analytics and using tag management solutions like Google Tag Manager.
- Setting Up Processes: A deliberate approach to setting up data processes facilitates ongoing data integrity. Regular checks and maintenance should be integrated into the strategy to ensure continuity and accuracy in data collection.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Building measurement strategies requires collaboration across departments. Marketing, IT, and sales teams must work together to ensure that the tools and processes put in place meets the needs of everyone involved.
- Continuous Evaluation: As the marketing landscape evolves, so too should measurement strategies. Regular reviews of data collection and analysis processes help identify weaknesses and opportunities for improvement.
Through building effective measurement strategies, brands can unlock the full potential of their data. Companies equipped with structured measurement systems can better anticipate market changes, adapt to consumer behavior, and optimize resource allocation. Ultimately, a well-devised strategy acts as the scaffolding that supports the entire structure of marketing measurement, paving the way for success.
Reporting and Evaluating Metrics
Reporting and evaluating metrics brand the Measurement Matrix as an integral component for understanding and improving marketing performance. This aspect emphasizes the storytelling power of data transforming raw numbers into narratives that reveal invaluable insights about business strategies.
The metrics collected during the data-building phase require careful examination to ascertain their implications for organizational performance. Effective reporting serves not only to present metrics but also to contextualize them within the larger scope of marketing goals. Engaging visual representations be it through graphs, dashboards, or infographics turn complex datasets into digestible formats that enhance stakeholder understanding.
To illustrate the importance of effective metrics reporting and evaluation, let’s dive into some core concepts:
- Traffic Metrics: Evaluating traffic metrics sheds light on the effectiveness of marketing channels. Metrics such as website visitors, page views, and referral sources help assess how well different channels are driving traffic to a site.
- Engagement Metrics: These metrics focus on user interactions. Bounce rate, session duration, and pages per session indicate how effectively content engages users and keeps them on the site.
- Conversion Metrics: The effectiveness of marketing efforts ultimately boils down to conversions. Evaluating metrics such as conversion rates and customer acquisition costs aids in understanding how well campaigns drive desired customer actions.
By embedding evaluation frameworks into the Reporting process, companies track their abilities against established KPIs. Regular assessment of these metrics allows organizations to identify trends and pinpoint areas for improvement. For instance, revealing low conversion rates might indicate a need for strategic refinements in a marketing campaign.
In essence, reporting and evaluating metrics serve as the bridge between raw data and actionable insights. By transforming data into coherent narratives, stakeholders can respond to performance outcomes with informed decisions that propel marketing strategies forward.
Types of Metrics to Report
When it comes to reporting the effectiveness of marketing initiatives, the choice of metrics plays a crucial role in informing decisions and shaping strategies. Different types of metrics unveil various dimensions of performance, each providing valuable insights that guide direction and prioritize actions.
Here are essential types of metrics that marketers should consider reporting:
- Traffic Metrics:
- Number of Visitors: Total visitors give a clear picture of reach and audience engagement over time.
- Traffic Sources: Understanding where visitors originate whether from organic searches, paid ads, or social media helps evaluate the effectiveness of each channel.
- Engagement Metrics:
- Bounce Rate: Indicates the percentage of visitors who leave without interacting, shedding light on the effectiveness of landing pages.
- Average Session Duration: Longer session duration typically suggests higher content engagement and user interest.
- Conversion Metrics:
- Conversion Rate: The ratio of total conversions to total visitors, critical for understanding campaign effectiveness.
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA): Monitoring the investment required to gain new customers allows for better budget allocations.
- Retention Metrics:
- Customer Retention Rate: Evaluates how many customers are retained over a certain period. This metric helps in assessing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Churn Rate: Indicates the rate at which customers stop doing business with a company, which can guide improvements in customer service and product offerings.
- Performance Metrics:
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating ROI gives insights into the profitability of marketing campaigns, further informing budgeting decisions.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Understanding the total worth a customer brings over their entire relationship with a business enables better long-term planning.
Different metrics paint distinctive pictures of marketing performance. Consequently, keeping a balance between various types of metrics enhances comprehensive evaluations that lead to finer adjustments in marketing strategies and more profound insights into customer behavior.
Best Practices for Reporting Results
To maximize the efficacy of reporting results within the Measurement Matrix, organizations should adhere to several best practices, ensuring clear communication and actionable insights emerge from data analysis. Drawing from experiences across industries, here are key guidelines to consider:
- Define Clear Objectives: Reporting should focus on answering critical business questions. Adopting the SMART framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) aids in creating targeted reports that align with business goals.
- Create Visual Dashboards: Utilize data visualization tools to present metrics in an engaging manner. Visual reports help stakeholders quickly absorb information and identify patterns, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Regular Review and Adaptation: Establish a routine for reviewing and updating reports. In the fast-changing landscape of marketing, ensuring relevance requires adaptability to new objectives, market conditions, and performance feedback.
- Engage Stakeholders: Collaborate with relevant teams during reporting phases. Involving stakeholders enhances buy-in and ensures reported metrics are aligned with varying departmental goals and perspectives, fostering cross-functional accountability.
- Interpret Data with Insights: Reports should not solely present numerical data; they should also interpret those numbers, offering actionable recommendations for strategic improvements. Analysts need to pinpoint trends, performance issues, and actionable opportunities.
- Establish Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for feedback on report effectiveness. Assessing how well reports communicate insights often yields suggestions for enhancements, improving future reporting efforts.
Following these best practices empowers organizations to create robust reports that elucidate data volume and context, paving the way to informed action and responsive marketing strategies. The clarity and relevance of reports can significantly affect marketing performance when stakeholders are equipped with actionable insights derived from comprehensive analyses.
Interpreting Data and Actionable Insights
The capability to interpret data effectively and extract actionable insights is fundamental to the success of the Measurement Matrix. Marketers must approach data analysis not just as a task but as a critical aspect of their overall marketing strategy. Understanding how to transform raw data into actionable information can often mean the difference between effective marketing and missed opportunities.
Marketers need to leverage statistical analysis tools and methodologies to delve deeper into data sets. This includes examining correlations, trends, and outliers to form a comprehensive view of performance metrics. For example, identifying a spike in traffic following a specific campaign might prompt further investigation into what resonated with audiences leading to the potential replication of that success in future initiatives.
Furthermore, actionable insights are not merely derived from quantitative data; qualitative insights from customer feedback, surveys, or focus groups can provide invaluable context. Integrating these insights into metrics analysis allows marketers to develop a more nuanced understanding of consumer sentiment and behavior, ultimately driving marketing efforts that resonate authentically with the target audience.
Key aspects of translating data into actionable insights include:
- Benchmarking Against Historical Data: Evaluating current performance against previous results can reveal trends and deviations. For instance, if a marketing campaign yields lower-than-expected engagement compared to prior efforts, it signals the need for a different approach or messaging.
- Segmenting Data: Analyzing data across different audience segments can uncover varying behaviors and preferences. Tailoring marketing strategies based on segmented insights enhances resonance and effectiveness in communicating with distinct consumer groups.
- Monitoring Changes Over Time: Understanding how performance metrics evolve over stretches of time grants insights into seasonality or campaign effectiveness, ensuring more strategic planning.
- Creating Action Plans: Based on data insights, actionable steps should be established. For instance, if low conversion rates are identified, building a targeted email campaign focused on those who engaged but did not convert can lead to actionable outcomes that drive engagement and sales.
The capacity to interpret data effectively ultimately shapes how a marketing team operates. When insights gleaned from analytics are utilized for continuous optimization, organizations position themselves to be adaptable, responsive, and ultimately more successful in achieving their marketing objectives.
Forecasting and Optimization Techniques
In the context of the Measurement Matrix, forecasting plays a pivotal role in driving marketing performance. Effective forecasting techniques empower organizations to prepare for future trends, customer behaviors, and market conditions based on historical data and predictive analytics. Much like navigating uncharted waters, forecasting offers a glimpse into the future allowing marketers to chart a course toward successful marketing initiatives.
A solid forecasting approach is built on accurate data collection, rigorous analysis, and the application of relevant models that fit specific business contexts. Here are several techniques that foster accurate forecasting:
- Time Series Analysis: This encompasses utilizing historical data to predict future trends based on observed patterns. Methods such as moving averages and exponential smoothing help create reliable forecasts by smoothing out fluctuations in data.
- Causal Models: This method incorporates external factors that may influence demand or sales, such as seasonality or economic indicators. Regression analysis often serves as a robust technique to isolate the influence of these variables on outcomes.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Advanced technologies increasingly enable marketers to employ machine learning techniques providing insights that can uncover hidden trends and complex relationships in data. These algorithms allow for dynamic adjustments in forecasting models, making them adaptable to shifts in real-time data patterns.
- Qualitative Forecasting: Techniques like focus groups, expert opinions, and customer interviews can yield qualitative insights that complement quantitative forecasts. Understanding consumer sentiment often plays a vital role in shaping accurate marketing strategies.
- Benchmarking Performance Metrics: Monitoring forecast accuracy through established benchmarks aids organizations in evaluating how well predictions correlate with real-world outcomes. Metrics such as Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) or Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) help in refining forecasting methodologies over time.
- Performance Monitoring: Establishing a framework for regularly assessing the effectiveness of forecasts allows organizations to adapt their strategies when predictions do not resonate with actual outcomes. This continuous feedback loop can significantly improve the accuracy of forecasting models.
By incorporating these techniques into their marketing strategies, organizations can anticipate changes in the marketplace and adjust their initiatives proactively. Ultimately, strong forecasting capabilities provide a roadmap for informed decision-making and strategic resource allocation, enabling organizations to navigate dynamic and competitive environments.
Techniques for Accurate Forecasting
While the importance of forecasting within the Measurement Matrix cannot be understated, the methods employed to achieve accuracy play a crucial role in determining the success of these efforts. In this section, we’ll explore specific techniques that lend themselves to creating more precise forecasting outcomes across a variety of marketing contexts.
- Trend Analysis: Carefully examining historical trends provides insights into seasonal behaviors and long-term patterns. Using data visualization techniques, marketers can represent these trends graphically, making it easier to identify recurring behaviors.
- Customer Segmentation: By segmenting customers based on various criteria such as demographics, purchasing behavior, or engagement levels marketers can forecast trends with more precision. Tailored approaches to different segments reveal distinct patterns that can enhance accuracy.
- A/B Testing: This technique not only helps optimize current campaigns but also provides valuable data for forecasting future performance. Marketers can compare the outcomes of varying strategies to determine which approaches yield better results.
- Pilot Programs: Rolling out small-scale pilot programs before a full launch allows marketers to evaluate performance metrics and customer responses. These insights can significantly influence forecasting accuracy for larger campaigns.
- Cross-Channel Analysis: Evaluating performance across various marketing channels can yield an understanding of holistic customer behaviors. Variability in performance across channels might impact forecast outcomes, as marketers can identify effective touchpoints.
- Integration of External Data: Incorporating external data related to market trends, economic indicators, or even competitor activities offers a broader perspective for accurate forecasting. Contextual data ensures that forecasts are not made in isolation, enhancing their overall reliability.
- Continuous Learning: As the market evolves, so should the forecasting methods. Regularly analyzing past forecasts and their outcomes creates a culture of learning. This adaptive approach allows teams to refine their predictions and make necessary adjustments.
By applying these techniques, marketers can create more informed and responsive strategies. The ability to forecast accurately signifies a business’s agility and preparedness in the face of market dynamics, fostering confidence among stakeholders and enhancing resource management.
Methods for Optimizing Marketing Efforts
Incorporating optimization techniques into marketing strategies is key to ensuring that resources are utilized effectively, and efforts yield maximum returns. With the Measurement Matrix providing a structured approach, marketers can utilize various methods to refine their campaigns continually. Here’s a detailed look at how optimization can be achieved:
- Dynamic Campaign Adjustments: Utilizing real-time data enables marketers to refine campaigns mid-flight. For example, if a specific ad group underperforms, swift adjustments such as reallocating budget or modifying creative elements can aid in improving performance.
- Leveraging A/B Testing: This iterative process allows marketers to test different campaign variables such as ad copy, landing pages, or audience targeting. By measuring the performance of each version, businesses can identify optimal setups, leading to improved results.
- Data-Driven Audience Targeting: Analyzing customer behavior helps marketers understand their audience segments better, allowing for targeted messaging. Enhanced targeting can lead to higher engagement rates and improved conversion metrics.
- SEO and Content Optimization: Regularly assessing website content for SEO effectiveness ensures that businesses maintain visibility on search engines. The use of keyword analytics helps marketers adapt their content strategies to current trends and consumer behavior.
- Remarketing Strategies: By re-engaging visitors who did not convert during their first interaction, marketers can capitalize on prior interest. Targeted remarketing campaigns help drive conversions from warm leads who have demonstrated some level of interest.
- Collaborative Feedback Loops: Facilitating cross-departmental reviews of marketing campaigns leads to broader insights. Receiving feedback from various perspectives such as sales, customer service, and digital teams fuels continuous improvement.
- Predictive Analytics Tools: Utilizing advanced predictive models to forecast future customer behavior empowers marketers to make informed decisions. These tools help identify which strategies are likely to drive successful outcomes based on historical patterns.
By adopting these methods, organizations can put an optimization framework in place that encourages iterative improvement. Optimization is an ongoing cycle within the Measurement Matrix that thrives on data-driven insights and responsiveness to market conditions.
Analyzing Trends Over Time
Understanding how marketing performance evolves over time is invaluable for organizations aiming to sustain competitive advantages. The Measurement Matrix facilitates this deep analysis, enabling marketers to visualize patterns, trends, and fluctuations in their initiatives. This section outlines key methodologies for effectively analyzing trends over time.
- Historical Comparisons: Analyzing past performance against current metrics allows marketers to identify trends in consumer behavior. By retaining historical records, teams can evaluate whether their strategies yield improving or declining results.
- Seasonal Trends: Identifying seasonal patterns can unlock valuable insights into how marketing initiatives should be adapted for specific times throughout the year. For example, an e-commerce company may observe significant spikes in online sales during holiday seasons informing marketing planning efforts.
- Longitudinal Studies: Establishing a continuous monitoring system allows for the collection of performance data over extended periods. Longitudinal studies yield insights into how customer behaviors shift and evolve, enabling businesses to adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Data Visualization Tools: Implementing data visualization techniques such as heat maps or trend lines allows stakeholders to quickly interpret performance metrics. This graphical representation creates awareness of trends that may not be immediately obvious in raw data.
- Surveys and Customer Feedback: Regularly gathering feedback can offer insights into changing customer preferences over time. By understanding shifts in attitudes and needs, organizations can fine-tune their marketing strategies to resonate more effectively.
- Market Research: Keeping abreast of industry trends through research reports, webinars, or professional networks helps marketers stay informed about external factors impacting consumer behavior.
- Cross-Reference Metrics: Examining various metrics in conjunction such as correlating email open rates with website traffic enables marketers to deduce interdependencies and understand which marketing efforts drive specific outcomes.
Through comprehensive trend analysis, organizations can make informed, data-driven decisions about their marketing strategies. By being attuned to evolving consumer behaviors and market shifts, businesses can adjust their tactics dynamically, ensuring greater success in meeting organizational objectives.
Tools and Technologies for Measurement
As marketing measurement matures, the role of tools and technologies remains pivotal in augmenting data accuracy and efficiency. They enable businesses to navigate through complex datasets and derive essential insights ready for actionable strategies. Here, we explore several prominent tools and technologies that enhance measurement efforts within the Measurement Matrix framework.
- Google Analytics: As a fundamental analytics platform, Google Analytics captures valuable data on user interactions, traffic sources, and engagement patterns. Metrics derived from this tool empower marketers to make informed decisions that drive better site performance.
- Google Tag Manager: GTM simplifies the management of tracking codes without requiring deep technical knowledge. This tool facilitates the implementation of various tags for services such as Google Ads and Google Analytics, streamlining the collection of tracking data.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Depending on the business size, integrating CRM platforms like Salesforce or HubSpot offers insights into customer interactions, categories, and purchasing trends, providing a well-rounded view of the customer lifecycle.
- Social Media Analytics Tools: Platforms like Hootsuite or Sprout Social allow marketers to monitor social engagement metrics, analyze campaign effectiveness, and gain insights into audience preferences based on social interactions.
- Data Visualization and Dashboard Tools: Utilizing visualization tools such as Tableau or Google Data Studio enables organizations to create interactive dashboards that present complex data in digestible formats, fostering data-driven decision-making.
- Email Marketing Analytics: Services like Mailchimp or Constant Contact provide analytics that gauge email campaign performance, giving insights into open rates, click-through rates, and conversions tied to specific email initiatives.
- Survey Tools: Platforms like SurveyMonkey or Typeform allow businesses to gather customer feedback, offering qualitative insights into customer preferences and perceptions of marketed products and services.
Among these tools, the Measurement Matrix encourages marketers to adopt an integrated approach utilizing multiple technologies in tandem to guarantee a seamless flow of data while maintaining high accuracy. When leveraged effectively, technologies serve as the backbone of marketing measurement, enabling teams to drive strategic initiatives with confidence.
Overview of Google Analytics
Google Analytics is heralded as an indispensable tool in the realm of digital marketing measurement. It allows businesses to track website performance, user engagement, and overall marketing ROI through data-driven insights. Below, we explore key features and functionalities that underscore its value.
- Data Collection Methods: Users install a tracking code on their websites that collects data on user interactions. This information encompasses page views, referral sources, geographical data, and session durations.
- Custom Reports: Google Analytics users can design customized reports tailored to specific KPIs. These reports can provide insights that are actionable based on particular business objectives, aiding in strategic planning.
- Real-Time Analytics: Real-time reporting allows marketers to monitor immediate user interactions, providing a window into how campaigns perform as they unfold, enabling rapid decision-making.
- User Segmentation: This feature allows marketers to segment audiences based on demographics, behavior, and channel interactions, enabling tailored targeting strategies geared toward different customer personas.
- Attribution Modeling: Google Analytics offers insights into how various marketing channels contribute to conversions. The ability to assign credit for conversions across multiple touchpoints significantly enhances understanding of customer journeys.
- Integration Capabilities: Google Analytics can seamlessly integrate with other tools like Google Ads, enabling marketers to understand the intricacies of paid campaigns. This interconnectedness fosters data sharing and cohesion across platforms.
With these capabilities, Google Analytics emerges as a powerful ally for marketers aiming to glean actionable insights from their data. The blending of data collection, analysis, and reporting empowers businesses to make informed decisions, optimizing their marketing strategies for greater efficacy.
Utilizing Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager (GTM) revolutionizes how marketers can manage tracking codes and measurement tags without in-depth technical expertise. This tool automates and streamlines the setup of various web analytics tags, making it easier to efficiently gather data relevant to marketing efforts. Here are key functionalities that highlight the significance of using GTM:
- Centralized Tag Management: GTM allows marketers to manage multiple tags from one dashboard, avoiding the confusion of potential misalignments or redundancies across numerous tags.
- Version Control: GTM enables users to maintain version histories of tags, providing functionality to revert to previous versions if necessary. This safeguard ensures that any errors can be remedied swiftly without significant downtime.
- Preview Mode: The preview mode is an excellent feature that allows marketers to test changes before going live. Ensuring that tags are firing correctly is critical to maintaining data accuracy.
- Event Tracking: GTM simplifies the process of implementing event tracking, enabling marketers to capture detailed interactions, such as clicks, form submissions, or video engagements. This data can be crucial for understanding user behavior.
- Custom Templates: Users can create custom templates or access community-contributed templates that streamline the tagging process. This flexibility saves time and reduces complexity in tag configurations.
- Seamless Integration: GTM integrates extensively with Google Analytics and various marketing platforms, ensuring that tags convey relevant data without a hitch. This is pivotal for businesses aiming to maintain a comprehensive view of their marketing performance.
By leveraging Google Tag Manager, organizations can maintain accuracy and efficiency in their data collection processes. Marketers benefit from a simplified setup, improved tagging management, and a more profound understanding of user interactions, ultimately enabling more nuanced marketing strategies.
Other Essential Measurement Tools
While Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager are pivotal to marketing measurement, various other tools can augment measurement efforts and provide deeper insights. Here’s a closer look at some essential measurement tools marketers should consider incorporating into their strategies:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Systems like Salesforce or HubSpot offer insights into customer interactions, providing a comprehensive view of the customer lifecycle. They facilitate tracking marketing campaigns’ effectiveness through sales performance metrics.
- Social Media Analytics Tools: Applications like Hootsuite and Sprout Social allow for tracking engagement metrics across social media platforms. These tools help marketers analyze campaign performance and understand audience sentiment more effectively.
- Email Marketing Tools: Platforms such as Mailchimp or Constant Contact come equipped with analytics for measuring email campaign performance, including open rates, click-through rates, and conversion metrics, providing insights into audience engagement.
- Survey and Feedback Tools: Tools like Typeform or SurveyMonkey enable marketers to collect qualitative data through customer feedback and sentiment analysis. Gleaning insights from customer opinions can inform product adjustments and marketing strategies.
- Data Visualization Tools: Software such as Tableau or Google Data Studio is crucial for translating raw data into engaging visual dashboards. These tools help stakeholders identify trends and performance metrics at a glance and foster data-driven decision-making.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Tools: Tools like Moz or SEMrush facilitate the analysis of website ranking and keyword performance, providing insights on how to enhance SEO efforts.
By integrating these essential measurement tools, marketers can establish a robust measurement framework that drives strategic decision-making. The synergy of various tools enhances data management and empowers organizations to derive actionable insights from diverse datasets.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Contextualizing the Measurement Matrix through real-world applications amplifies its relevance in marketing strategies. Organizations often face unique challenges, making their solutions critical to understanding the practicality of the framework. Here, we highlight several notable instances of successful implementations of the Measurement Matrix.
- Starbucks: By leveraging data-driven analytics, Starbucks tracks customer preferences and purchase behaviors within its loyalty program. This enables the coffee giant to personalize marketing efforts and adjust menu offerings based on consumer demand.
- Netflix: To retain subscribers, Netflix employs its recommendation system, dynamically analyzing user patterns and preferences to curate personalized content suggestions. This technique drives the majority of viewer engagement and aids in subscriber retention strategies.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola invested heavily in predictive analytics to comprehend consumer trends and attitudes. By gathering and analyzing data from diverse sources, Coca-Cola adapts its marketing strategies in real time, ensuring that product offerings reflect current consumer desires.
- American Express Global Business Travel (GBT): Faced with performance challenges, Amex GBT overhauled its analytics platform, enabling faster scalability and engagement through enhanced user experiences. Implementing a more robust data infrastructure facilitated improved spend notifications and boarding times.
- Airline Solutions Company: This organization developed an enterprise travel data warehouse, allowing for real-time market analysis of customer behavior. The results led to prompt responses to shifts in demand and operational performance, demonstrating a commitment to responsive service.
These case studies exemplify how organizations have successfully harnessed the Measurement Matrix to achieve tangible results. Transformative approaches to measurement facilitated improved decision-making and increased accountability, showcasing the criticality of a robust measurement framework tailored to individual business contexts.
Common Challenges and Resolutions
While implementing the Measurement Matrix can yield significant benefits, organizations often encounter challenges when navigating measurement marketing. Here are several common obstacles and their corresponding resolutions based on real-world experiences.
- Data Overload: Many businesses struggle with the sheer volume of data generated by various sources. To combat this, organizations should focus on identifying key metrics that align with their objectives, ensuring only relevant data drives decision-making.
- Lack of Clear Objectives: Unclear or misaligned objectives can complicate measurement initiatives. Implementing a structured planning phase, such as the Q.I.A. framework, can provide clarity and ensure marketing efforts are purpose-driven.
- Technical Expertise: Not all marketers possess technical proficiency in data management or analytic tools. Investing in training programs or enlisting specialists when necessary can help teams better utilize measurement tools effectively.
- Inefficient Reporting: Teams may struggle to derive actionable insights from reporting processes. Establishing standards for data presentation (e.g., utilizing dashboards) and fostering cross-departmental dialogue ensures more coherent communication surrounding performance metrics.
- Slow Adaptation to Feedback: Organizations often miss opportunities for improvement by failing to act on insights quickly enough. Once feedback mechanisms are established, instituting an iterative process for strategy adjustments promotes agility.
By addressing these common challenges, organizations can significantly improve their marketing measurement practices. The iterative cycle of planning, building, reporting, and optimizing creates a dynamic framework that fosters continuous learning and adaptation critical components for blockchain success in measurement marketing.
Lessons Learned from Case Studies
The practical applications of the Measurement Matrix yield valuable lessons applicable across various sectors. Reflecting on the experiences of organizations that successfully implemented the framework, we find noteworthy takeaways that can guide future endeavors.
- Embrace Data-Driven Culture: A commitment to leveraging data for decision-making fosters a culture of accountability. Organizations that prioritize analytics tend to experience improved outcomes, as stakeholders recognize the importance of informed strategies.
- Flexibility is Crucial: The ability to pivot in response to data insights enhances organizational resilience. Companies that demonstrate adaptability can more effectively address shifts in market demands and customer preferences.
- Building Infrastructure Takes Time: Developing a robust measurement framework is iterative, and organizations must remain patient throughout this process. Investing in technology and skill development upfront can yield long-term benefits.
- Collaboration Enhances Strategies: Successful implementations showcase the value of interdepartmental collaboration. When teams work together, insights are shared, leading to a more holistic view of marketing performance.
- Continuous Learning and Iteration: Regular assessments of strategies and results are essential. Marrying insights gained with an agile framework allows organizations to continually refine their approaches, promoting innovation.
By synthesizing these lessons, marketers can create comprehensive strategies that embrace collaboration and continual improvement while maximizing the effectiveness of their measurement practices. The Measurement Matrix becomes more than just a tool it symbolizes a cultural shift towards data-driven decision-making.
Expert Insights and Recommendations
Chris Mercer’s work in measurement marketing encapsulates invaluable insights that can support organizations striving for better measurement and performance outcomes. He shares essential recommendations that advance robust strategies grounded in actionable data:
- Comprehensive Measurement Strategy: Mercer underscores the importance of identifying metrics that align with business goals. Each metric should have a clear purpose in the context of overall objectives to ensure informed decision-making.
- Plan-Build-Launch Framework: A structured approach streamlined by planning, building, and executing measurements leads to future-proofing initiatives. This ensures campaigns are responsive to the data collected, effectively adapting based on insights.
- Emphasis on Dashboards: Creating dashboards that deliver clear insights avoids overwhelming users with excessive data. Well-designed dashboards focus on critical performance indicators empowering stakeholders to make informed choices efficiently.
- Ongoing Education: The rapid evolution of digital marketing necessitates continuous learning. Engaging in training, workshops, and forums such as MeasureSummit equips marketers with the latest trends and techniques in measurement marketing.
- Utilizing Data Optimization: Organizations should cycle through the process of analyzing data insights with a mind for supporting optimization strategy. Refinements born from insights lead to more significant gains and enhanced performance metrics.
By adopting these expert recommendations, organizations can reinforce their measurement practices, ensuring they maximize the potential of data to drive effective marketing strategies. Chris Mercer’s methodologies encourage marketers to leverage data as a catalyst for actionable insights that foster long-term success.
Chris Mercer’s Approach to Measurement Marketing
Chris Mercer’s approach to measurement marketing fuses creativity with data-driven strategies, creating a robust framework for marketers to thrive in increasingly complex environments. His methodology offers compelling direction for organizations looking to leverage actionable insights effectively. Here’s an exploration of his strategic principles:
- Focus on Purposeful Measurement: Mercer emphasizes the need for marketers to identify key outputs relevant to their goals. By concentrating on metrics that reflect organizational objectives, the potential for actionable insights grows.
- Structured Measurement Framework: The unique Plan-Build-Launch methodology is core to Mercer’s approach, ensuring that insights gleaned during the measurement process directly inform marketing activities. This cyclical model creates an adaptable structure.
- Clear Communication of Insights: Creating easily interpretable dashboards turns complex data into clear narratives that resonate with stakeholders. By shaping insights into coherent stories, marketers can effectively communicate performance outcomes.
- Informed Decision-Making: Promoting a culture of data-driven decision-making enables marketers to leverage insights actively. By relying on a systematic methodology, organizations ensure they excel in navigating unpredictable market shifts.
- Continuous Optimization: Mercer advocates for ongoing adjustments based on data insights, underlining the importance of remaining flexible. Leveraging feedback to refine marketing strategies ensures organizations remain competitive and responsive to change.
- Integration of Education: Mercer’s work encourages education around measurement marketing practices and tool utilization for stakeholders. This ongoing learning fosters adaptability and equips teams with the skills needed to harness data effectively.
Through this comprehensive approach, Mercer aims to empower marketers by ensuring they are equipped to maximize the potential of their data. By enabling a deeper understanding of metrics and fostering a culture of continuous learning, organizations can cultivate an environment primed for sustained success.
Future Trends in Marketing Measurement
The landscape of marketing measurement continues to evolve, influenced by technological advancements and changes in consumer behavior. As we peer into the future, several trends are emerging that can shape measurement practices moving forward. Some key trends include:
- Privacy-Centric Measurement: A noticeable shift towards consumer data privacy demands that organizations adapt their measurement protocols to comply with new regulations. This evolution necessitates the adoption of privacy-safe technologies that provide transparent data collection methods while still generating actionable insights.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: The infusion of AI tools into marketing measurement allows for enhanced data analytics, enabling predictive capabilities and deeper insights. Marketers can harness machine learning algorithms to detect patterns and shift strategies dynamically.
- Holistic Customer Journey Tracking: Brands will increasingly focus on measuring complete customer journeys that span multiple touchpoints. This holistic view helps to accurately attribute marketing efforts to tangible business outcomes, reflecting the complexities of consumer decision-making.
- Emphasis on Commercial Intelligence: As organizations integrate brand, customer, product, and operational factors into measurement practices, the relevance of commercial intelligence will burgeon. Breaking down silos enables a more comprehensive understanding of how various elements contribute to overall performance.
- Collaborative Measurement Cultures: Organizations that emphasize cross-functional collaboration in measurement efforts will enjoy greater analytical insights. Promoting teamwork guarantees that diverse perspectives are incorporated into data analysis, encouraging holistic strategies that benefit all departments involved.
- More Agile Measurement Techniques: The market’s rapid evolution necessitates more agile measurement techniques that adapt to changing conditions. Flexible approaches to data capture will allow businesses to remain responsive while still aligning with strategic goals.
As organizations embrace these emerging trends, they position themselves to navigate future complexities confidently. The ability to adapt to evolving measurement practices will be paramount in ensuring that marketing strategies yield meaningful and effective results, fostering long-term business resilience.
Building a Measurement Culture Within Organizations
The successful implementation of the Measurement Matrix framework pivots on establishing a measurement culture within organizations. Fostering an environment that embraces data-driven decision-making creates a fertile ground for marketing effectiveness. Here are several strategies to cultivate this culture:
- Executive Buy-In: Leadership endorsement is paramount for establishing a measurement culture. When executives prioritize measurement and analytics, it underscores its importance and encourages employees at all levels to integrate data into their workflows promptly.
- Comprehensive Training Initiatives: Providing ongoing training and resources equips teams with the knowledge and skills necessary to leverage measurement tools effectively. Workshops, certifications, and knowledge-sharing sessions can enhance employees’ confidence in utilizing data.
- Encouragement of Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Promoting collaboration among various departments fosters a sense of shared ownership over measurable outcomes. Encouraging input from sales, customer service, and product teams ensures a more enriched perspective on overall business performance.
- Celebrating Data-Driven Wins: Recognizing and celebrating the successes achieved through measurement efforts cultivates enthusiasm for data-driven initiatives. Highlighting case studies and sharing positive results reinforces the value of measurement culture.
- Establishing Clear Metrics: Organizations should develop clear, accessible metrics that align with business goals. When employees understand the metrics tied to their roles, they can better align their activities with broader business objectives.
- Facilitating Open Communication: Creating open channels for communication surrounding measurement offers teams the opportunity to share insights, ask questions, and engage in discussions. This environment encourages inquiry and promotes a greater understanding of data-driven decision-making.
By embedding a measurement culture within organizations, teams can operate with a shared commitment to objectives. The ability to utilize data effectively strengthens strategies, enhances accountability, and ultimately leads to measurable success over time.
In conclusion, the Measurement Matrix by Chris Mercer proves to be an invaluable framework for modern marketing strategies. By emphasizing structured approaches to planning, building, reporting, and optimizing, organizations can harness the potential of data to drive success in an ever-evolving marketplace. With the blend of strategic insights, measurement tools, and forward-thinking methodologies, businesses are set to navigate the intricate landscape of marketing measurement effectively. Implementing these principles today prepares organizations for an adaptive future in which data not only informs decision-making but drives innovation and growth.

Frequently Asked Questions:
Business Model Innovation:
Embrace the concept of a legitimate business! Our strategy revolves around organizing group buys where participants collectively share the costs. The pooled funds are used to purchase popular courses, which we then offer to individuals with limited financial resources. While the authors of these courses might have concerns, our clients appreciate the affordability and accessibility we provide.
The Legal Landscape:
The legality of our activities is a gray area. Although we don’t have explicit permission from the course authors to resell the material, there’s a technical nuance involved. The course authors did not outline specific restrictions on resale when the courses were purchased. This legal nuance presents both an opportunity for us and a benefit for those seeking affordable access.
Quality Assurance: Addressing the Core Issue
When it comes to quality, purchasing a course directly from the sale page ensures that all materials and resources are identical to those obtained through traditional channels.
However, we set ourselves apart by offering more than just personal research and resale. It’s important to understand that we are not the official providers of these courses, which means that certain premium services are not included in our offering:
- There are no scheduled coaching calls or sessions with the author.
- Access to the author’s private Facebook group or web portal is not available.
- Membership in the author’s private forum is not included.
- There is no direct email support from the author or their team.
We operate independently with the aim of making courses more affordable by excluding the additional services offered through official channels. We greatly appreciate your understanding of our unique approach.
Be the first to review “The Measurement Matrix with Chris Mercer” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.